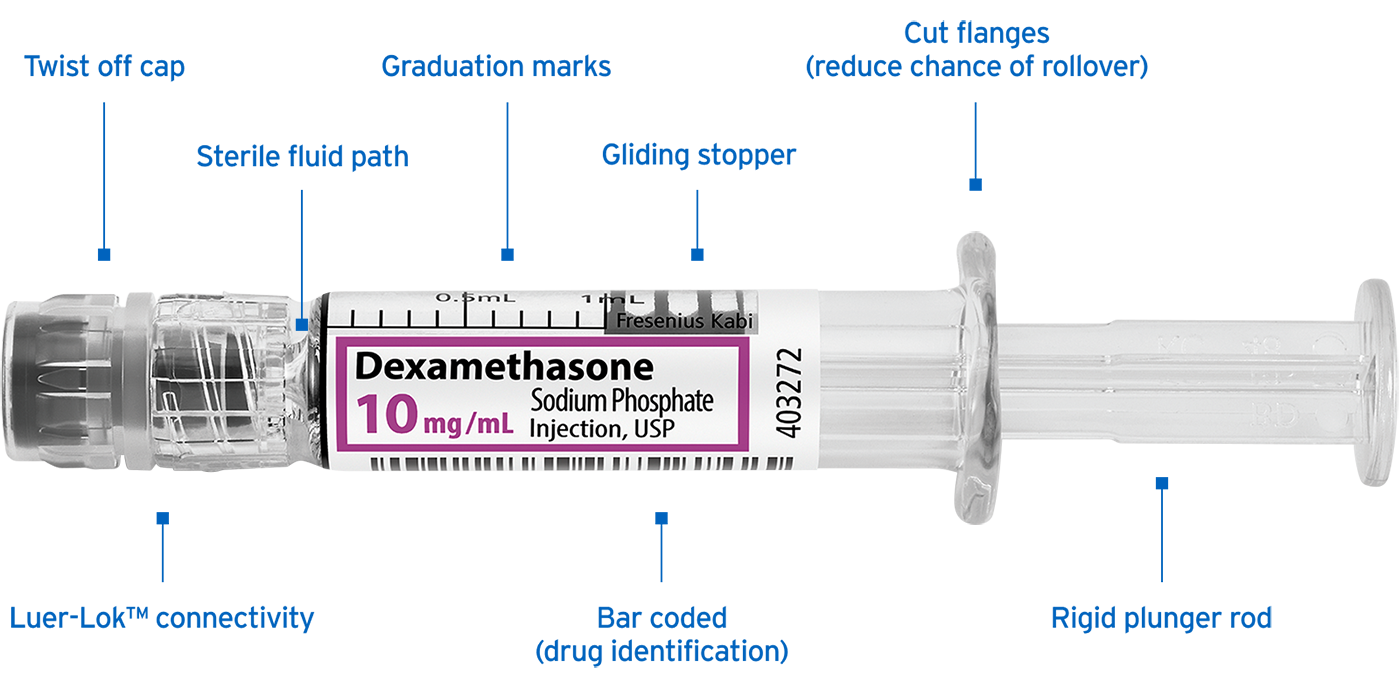
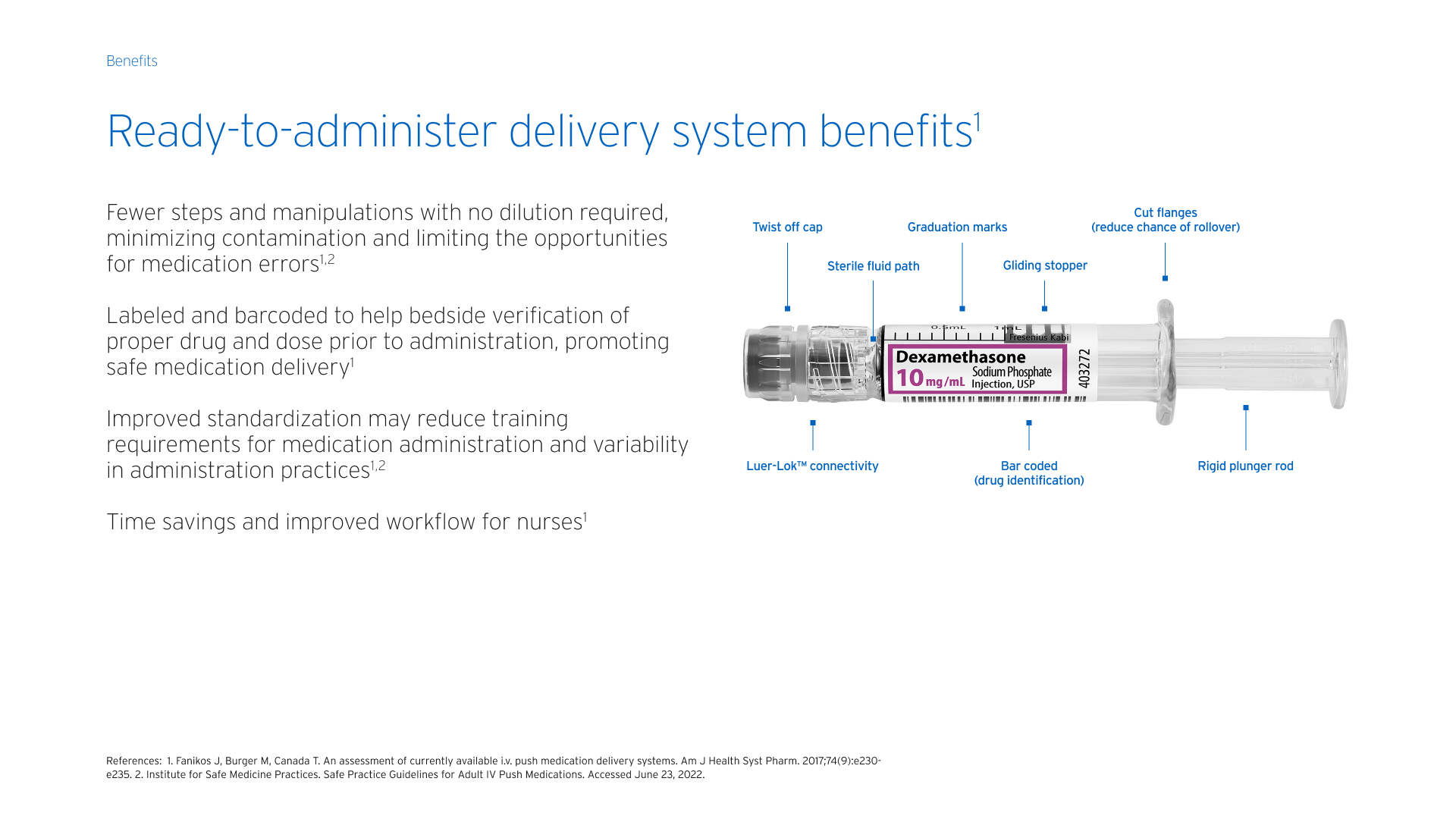
Primary Literature > Intraoperative Opioid Waste and Association of Intraoperative Opioid Dose with Postoperative Adverse Outcomes: A Hospital Registry Study
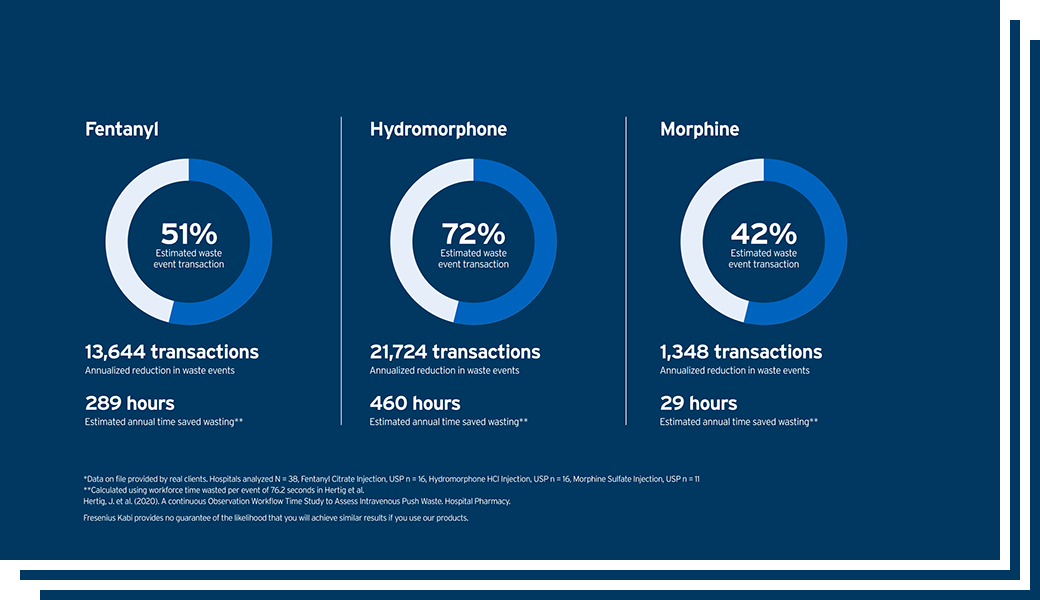
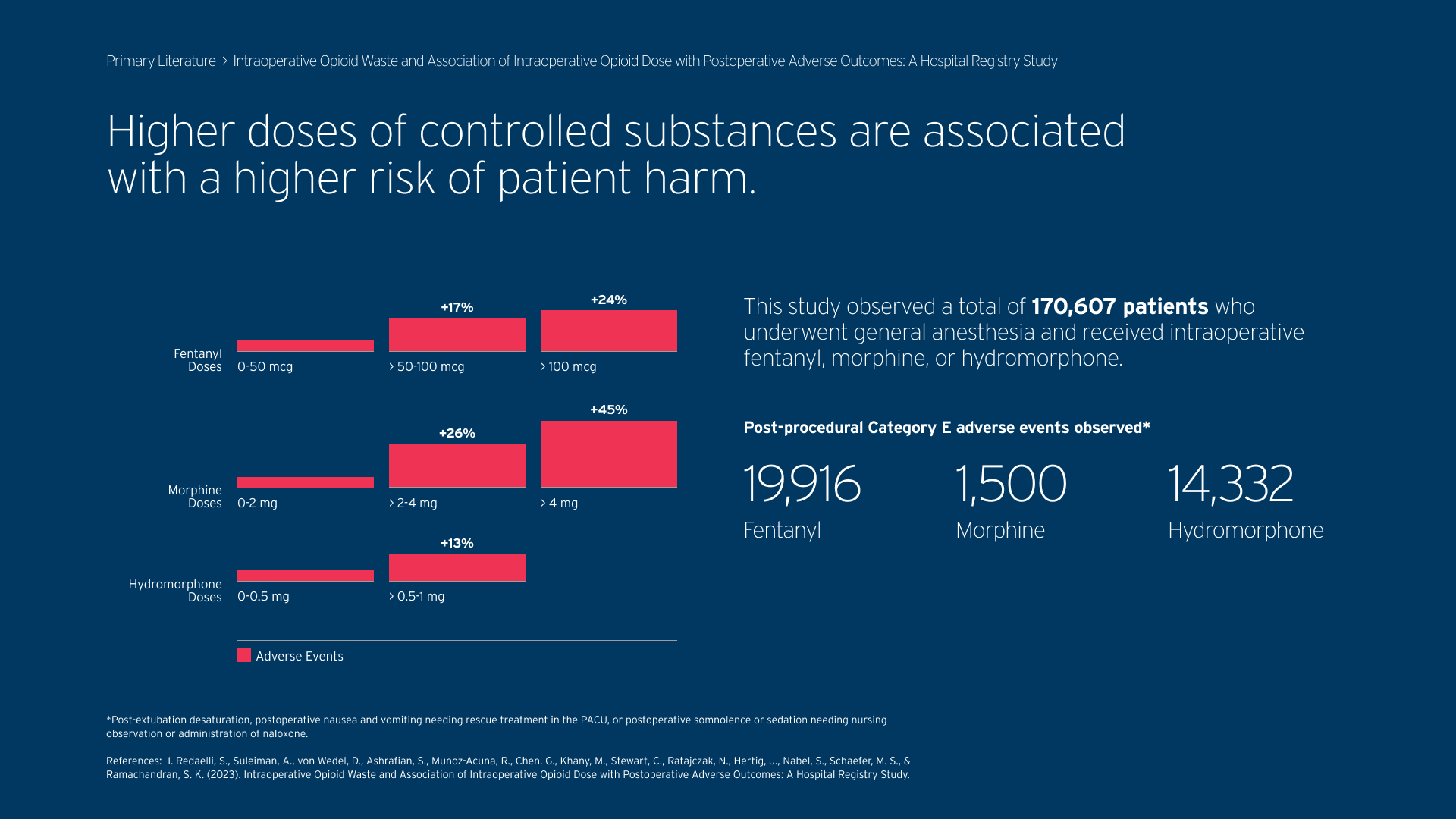
This study observed a total of 170,607 patients who underwent general anesthesia and received intraoperative fentanyl, morphine, or hydromorphone.
Post-procedural Category E adverse events observed*
*Post-extubation desaturation, postoperative nausea and vomiting needing rescue treatment in the PACU, or postoperative somnolence or sedation needing nursing observation or administration of naloxone.
References: 1. Redaelli, S., Suleiman, A., von Wedel, D., Ashrafian, S., Munoz-Acuna, R., Chen, G., Khany, M., Stewart, C., Ratajczak, N., Hertig, J., Nabel, S., Schaefer, M. S., & Ramachandran, S. K. (2023). Intraoperative Opioid Waste and Association of Intraoperative Opioid Dose with Postoperative Adverse Outcomes: A Hospital Registry Study.